
John D. Kanu
jdkanu@cs.umd.edu
I am a 2nd-year graduate student in Computer Science at the University of Maryland, College Park. I am interested in the intersection of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotics.
Preprints
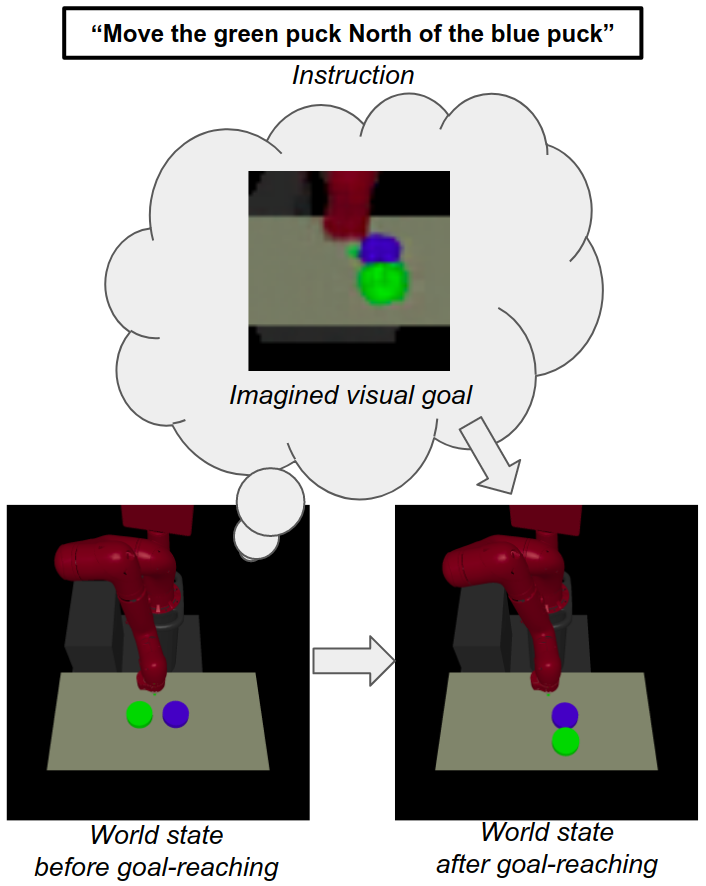
Following Instructions by Imagining and Reaching Visual Goals
John D. Kanu, Eadom Dessalene, Xiaomin Lin, Yiannis Aloimonos. arXiv. [arXiv] [code]
While traditional methods for instruction-following typically assume prior linguistic and perceptual knowledge, many recent works in reinforcement learning (RL) have proposed learning policies end-to-end, typically by training neural networks to map joint representations of observations and instructions directly to actions. In this work, we present a novel framework for learning to perform temporally extended tasks using spatial reasoning in the RL framework, by sequentially imagining visual goals and choosing appropriate actions to fulfill imagined goals. Our framework operates on raw pixel images, assumes no prior linguistic or perceptual knowledge, and learns via intrinsic motivation and a single extrinsic reward signal measuring task completion. We validate our method in two environments with a robot arm in a simulated interactive 3D environment. Our method outperforms two flat architectures with raw-pixel and ground-truth states, and a hierarchical architecture with ground-truth states on object arrangement tasks.
Publications
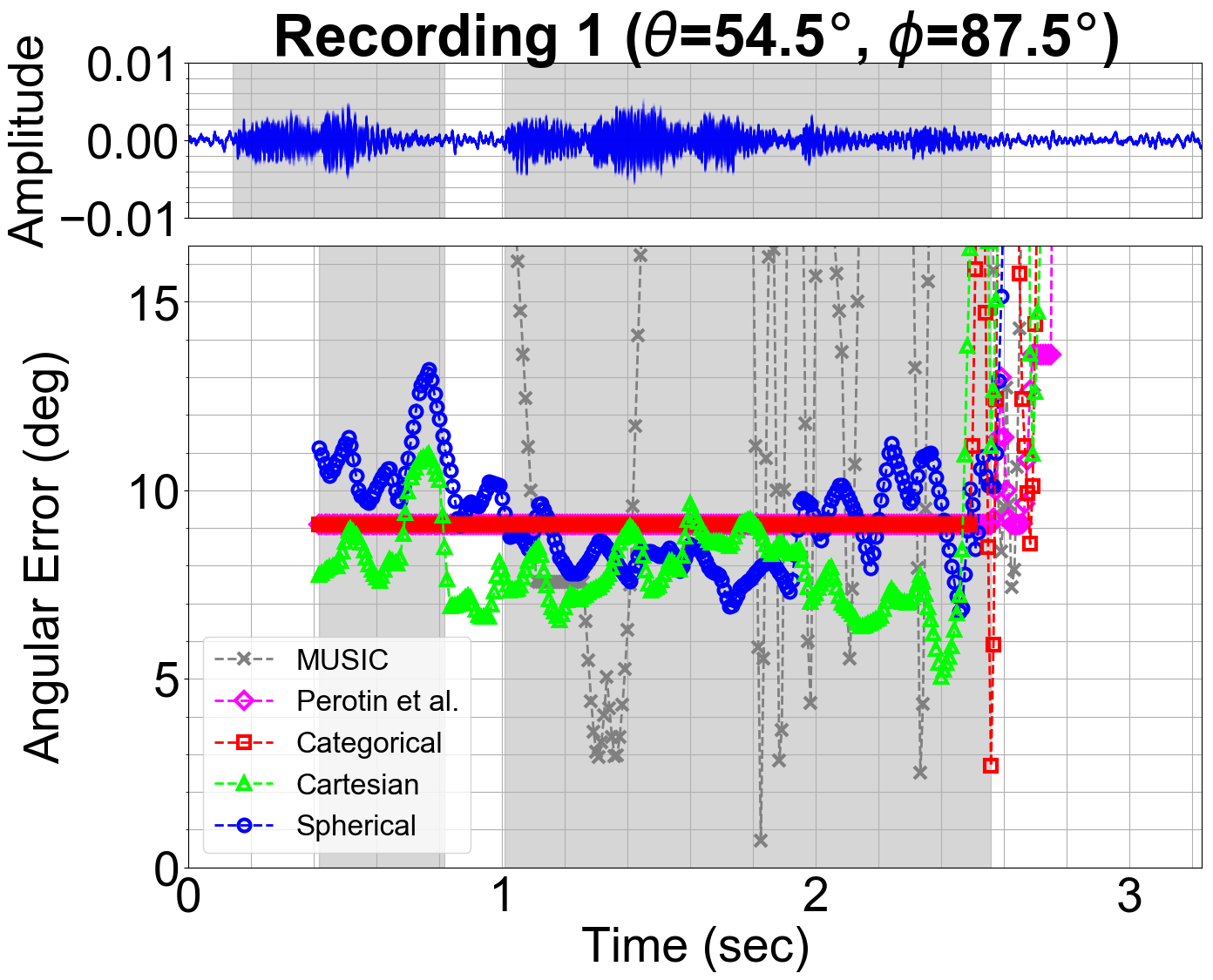
Regression and Classification for Direction-of-Arrival Estimation with Convolutional Recurrent Neural Networks
Zhenyu Tang, John D. Kanu, Kevin Hogan, Dinesh Manocha. Interspeech 2019. [arXiv] [code]
We present a novel learning-based approach to estimate the direction-of-arrival (DOA) of a sound source using a convolutional recurrent neural network (CRNN) trained via regression on synthetic data and Cartesian labels. We also describe an improved method to generate synthetic data to train the neural network using state-of-the-art sound propagation algorithms that model specular as well as diffuse reflections of sound. We compare our model against three other CRNNs trained using different formulations of the same problem: classification on categorical labels, and regression on spherical coordinate labels. In practice, our model achieves up to 43% decrease in angular error over prior methods. The use of diffuse reflection results in 34% and 41% reduction in angular prediction errors on LOCATA and SOFA datasets, respectively, over prior methods based on image-source methods. Our method results in an additional 3% error reduction over prior schemes that use classification based networks, and we use 36% fewer network parameters.
Teaching
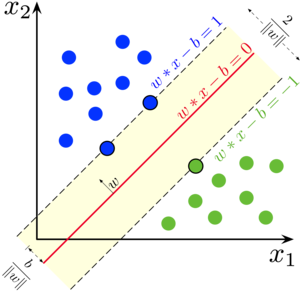
CMSC422: Introduction to Machine Learning
Graduate Teaching Assistant
Professor James Reggia
University of Maryland, College Park
Spring 2019

CMSC422: Introduction to Machine Learning
Graduate Teaching Assistant
Professor William Regli
University of Maryland, College Park
Fall 2018
CMSC421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
Undergraduate Teaching Assistant
Professor James Reggia
University of Maryland, College Park
Spring 2018

CMSC422: Introduction to Machine Learning
Undergraduate Teaching Assistant
Professor James Reggia
University of Maryland, College Park
Fall 2017

CMSC421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
Undergraduate Teaching Assistant
Professor Don Perlis
University of Maryland, College Park
Spring 2017

CMSC422: Introduction to Machine Learning
Undergraduate Teaching Assistant
Professor V.S. Subrahmanian
University of Maryland, College Park
Fall 2016